What is Gout?
Gout, a form of arthritis, is a disease that has plagued man for hundreds of years and continues to do so today. It is caused by too much uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a natural waste product that occurs when your body breaks down certain types of foods such as organ meats, which contain a class of chemicals called purines. Due to a deficiency of the digestive enzyme uricase, people who have gout are unable to break down and excrete uric acid, allowing levels of it to build up in the blood, a condition called hyperuricemia. Thus, uric acid crystals accumulate in the body’s connective tissue in and around joints, causing pain and swelling. Uric acid crystals can also collect in the kidneys and lead to kidney stones and eventually kidney failure.
Who Suffers from Gout
Approximately two million people suffer with gout, with between 75-90% being middle-aged men. Women usually get gout only after menopause, possibly due to the drop in estrogen women experience after menopause.
What Causes Gout
There are numerous risk factors that are associated with gout, such as:
- Alcohol consumption: drinking too many alcoholic drinks can lead to hyperuricemia because alcohol interferes with the removal of uric acid from the body.
- Diet: Eating too many foods rich is purines can cause gout in some people.
- Gender & Age: Men are more susceptible to gout than women. Children rarely get gout.
- Genetics: Twenty percent of people with gout have a family history.
- Health Problems: other health problems can lead to gout, such as high blood pressure, hypothyroidism, psoriasis, hemolytic anemia, or even some cancers.
- Kelley-Seegmiller Syndrome or Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: two rare conditions in which the enzyme that helps control uric acid levels either is not present or is found in insufficient quantities in the body.
- Lead Exposure: sometimes lead exposure can cause gout.
- Medications: Many medications may increase the chance of a person developing gout:
- Cyclosporine: a medication that suppresses the body’s immune system, used to treat some autoimmune diseases and to prevent the body’s rejection of transplanted organs.
- Diuretics: drugs such as furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide, and metolazone, which are taken to eliminate excess fluid from the body.
- Levodopa: a medication that is used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
- Niacin
- Salicylate containing drugs: aspirin
- Renal Insufficiency: the inability of the kidneys to eliminate waste products.
- Weight: Obesity increases the risk of developing gout because there is more tissue available for breakdown, which leads to excess uric acid production.
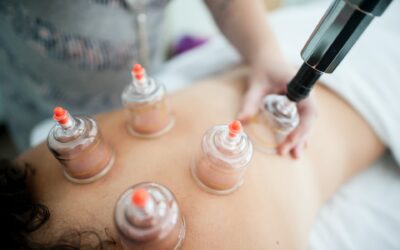
Gout Hijama
Carefully placing cups on relevant points will help eliminate the pain caused from gout thus reducing the overall gout.
OVER 10K HAPPY CLIENTS ACROSS THE UK INCLUDING BIRMINGHAM, WALSALL, DUDLEY, STOURBRIDGE, OLDBURY, WOLVERHAMPTON, COVENTRY, LEAMINGTON SPA, NOTTINGHAM, SOLIHULL, TELFORD, GLOUCESTER, WORCESTER, DERBY, BRISTOL, STOKE AND SUTTON COLDFIELD INCLUDING THE FOLLOWING AREAS:
Acocks Green, Alum Rock, Aston, Balsall Heath, Birmingham City Centre, Bordesley Green, Bromford, Castle Vale, Digbeth, Edgbaston, Erdington, Garretts Green, Great Barr, Hall Green, Handsworth, Harborne, Hay Mills, Highgate, Hockley, Hodge Hill, Jewellery Quarter, King's Heath, Kings Norton, Kingstanding, Kitts Green, Ladywood, Lozells, Moseley, Nechells, Newtown, Northfield, Nuneaton, Pelham, Perry Barr, Quinton, Saltley, Selly Oak, Selly Park, Shard End, Sheldon, Small Heath, Smethwick, South Yardley, Sparkbrook, Sparkhill, Stechford, Tipton, Tyseley, Ward End, Washwood Heath, Wednesbury, West Bromwich, Winson Green, Witton, Yardley, Yardley Wood
Our therapists are fully insured for all services we provide. Qaya Clinic is based in Edgbaston Medical Village, Birmingham City Centre. WE ARE OUTSIDE THE CLEAN AIR ZONE with free nearby parking.